Home / Blog / Fundamentals / Internal Linking Best Practices: Mastering SEO Through Effective Linking
Internal Linking Best Practices: Mastering SEO Through Effective Linking
Nov 28, 2023
Share to
Internal links are a crucial element in optimizing your website for search engines. They not only facilitate smoother navigation for users and search engines across your site’s content and structure but also significantly impact your SEO performance.
This comprehensive guide covers all aspects of internal linking. You’ll learn about the nature of internal links, their role in enhancing SEO, the importance of anchor text, and effective strategies for implementing an internal linking plan. Additionally, it includes a list of best practices and practical tips — the Dos and Don’ts — to ensure your internal linking strategy is both effective and efficient.

What Are Internal Links?
Internal links are hyperlinks that connect one page of a website to another page within the same domain. For example, a link embedded in the text on “www.exampleabc.com/home” that directs a user to “www.exampleabc.com/service-page-1” is an internal link. These links are integral in structurally organizing your website, allowing users to navigate effortlessly between different pages and sections.
Distinguishing Internal Links from External Links and Backlinks
While internal links are pivotal for in-site navigation, they differ significantly from external links and backlinks. An external link is when your website includes a hyperlink that points to a page on a different domain. For instance, a reference on your site that leads to another company’s page is an external link. It connects your domain to the wider internet, providing users with additional resources or information.
On the other hand, backlinks are links that come from external websites and point back to your site. They are crucial for SEO as they suggest to search engines that other websites endorse or find your content valuable. A link from a different website, say “www.otherdomain.com,” directing users to your site (“www.mysite.com“), is a backlink.
Is Internal Linking Good for SEO?
During the Office hour session, John Muller confirmed that internal links are critical for SEO and help users and Googlebot understand the importance of page pages.
Internal links are incredibly beneficial for the two key visitors to your site: search engines and human users. These links simplify the process for search engines to crawl and comprehend the layout of your website. Concurrently, they aid users in effortlessly finding relevant and insightful content.
Here’s a breakdown of how internal links enhance your website’s functionality:
1. Helps Search Engines Understand Site Structure
Internal links effectively establish a hierarchy or roadmap for your website. As search engine crawlers navigate through your site, they follow these links to traverse between different pages. This activity enables them to discern the relative importance of each page. Essentially, the more frequently a page is linked within the site, the greater its perceived importance.
Take your website’s menu as an example. It typically includes links to key pages, but not to every single page on the site. This selective linking strategy signals to search engines which pages are of higher priority, influencing how they assess and value each page.
Additionally, most websites utilize their menus, as well as footer sections, to highlight categories, essential pages, and other significant links. Internal links play a crucial role here, not just in connecting obvious pages, but also in integrating more intricate or less prominent pages of your site into the overall structure. This connectivity ensures a comprehensive and accessible website architecture, both for users and for search engines.
2. Enhances the User Experience
Internal links significantly enhance the navigational experience for users on your website. When visitors encounter relevant links within the content they are reading, they can effortlessly click through to additional information or related pages. This capability allows users to explore your site more deeply, accessing the information they need without relying solely on the main navigation menu.
When employed strategically and with consideration, internal links can effectively guide users through your website, maintaining their engagement and aiding them in finding the necessary information. This thoughtful approach to internal linking can greatly increase user satisfaction and site usability.
For instance, in our blog post about meta titles, we included internal links to our own tools designed to assist SEO professionals in crafting better meta titles and descriptions. Such links not only provide immediate value to the reader but also encourage further exploration of your site’s offerings.

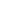
Wikipedia pages serve as an excellent illustration of effective user engagement through internal linking. As users navigate a Wikipedia article, they encounter hyperlinks on key terms and concepts, guiding them seamlessly from one topic to another. This strategy helps in keeping users engaged and encourages them to spend more time exploring the site.
The abundance of links on a Wikipedia page is possible because of its vast, community-driven content base. Each link is carefully placed to ensure relevance and contextuality, connecting users to other pertinent articles within the Wikipedia ecosystem.
When implementing a similar strategy on your website, it’s vital to ensure that your internal links are equally relevant and context-specific. The goal is to connect essential and related content in a way that enhances the user’s journey, providing value without overwhelming them with unnecessary or irrelevant links. This thoughtful approach to internal linking not only improves user engagement but also reinforces the coherence and authority of your site’s content.
3. Drives Higher Conversions
A superior user experience often translates into increased user satisfaction, which in turn can lead to higher conversion rates.
But what role do internal links play in enhancing conversions? Let’s explore, especially in the context of an eCommerce setup. Internal links can be a powerful tool for eCommerce brands to boost conversions. They facilitate smooth navigation for users across various pages, categories, and stages of the marketing funnel.
Consider internal linking as a form of content mapping, where a strategic approach is aligned with the buyer’s journey. The key is to identify (or create) the right pieces of content and link them in a manner that guides users through the different funnel stages — from the top of the funnel (ToFu) to the middle of the funnel (MoFu) and bottom of the funnel (BoFu).
Effective internal linking, particularly from content at the early stages of the funnel, can significantly drive your audience deeper into the conversion process. This not only enhances user engagement but also potentially increases revenue, as users are smoothly led from initial awareness to the point of purchase.
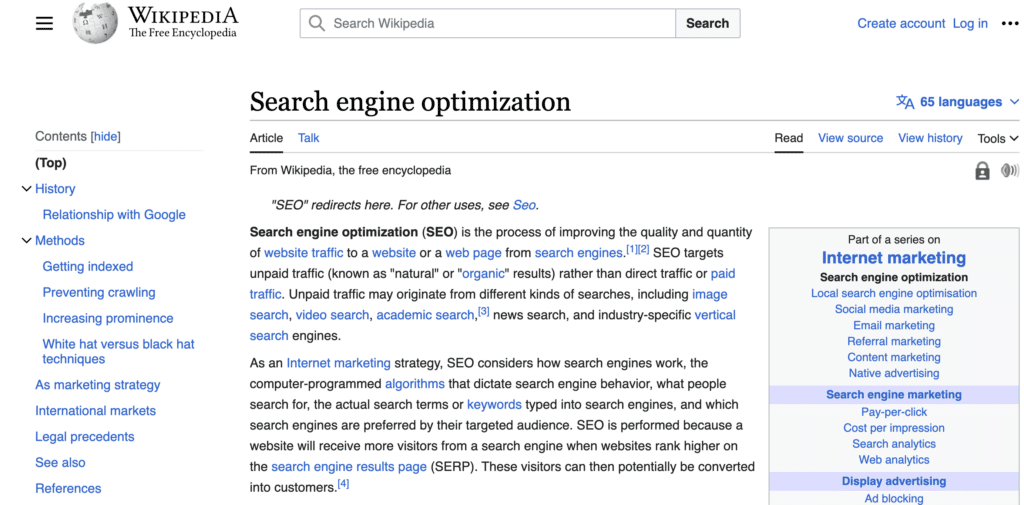
4. Improves Crawl Efficiency and Helps in Indexing
In the documentation of how Google search works, they clearly mention, “Some pages are known because Google has already visited them. Other pages are discovered when Google follows a link from a known page to a new page.”
Internal links play a pivotal role in enhancing the efficiency with which search engine crawlers navigate (or “crawl”) through your website. This process is crucial for two main reasons: improving crawl efficiency and aiding in the indexing of your web pages.
- Improving Crawl Efficiency – Crawl efficiency refers to how effectively search engine bots can scan and analyze the content of your website. Well-structured internal linking ensures that crawlers can easily find and access all the pages on your site. Without such interconnectedness, some pages might remain hidden or isolated, making it harder for search engines to discover and understand them. Efficient crawling is particularly important for large websites or those that frequently update their content.
- Aiding in Indexing – Indexing is the process by which search engines organize information before a search to enable fast and accurate responses to user queries. By using internal links, you help search engines understand the structure and hierarchy of your site. The more efficiently a search engine can crawl and comprehend your site, the more accurately it can index your pages. This improved indexing is vital for your pages to appear in relevant search results.
In summary, internal links not only contribute to a better user experience but are also instrumental in ensuring that search engines can efficiently crawl and index your site. This leads to better visibility in search engine results, enhancing your site’s overall online presence.
5. Internal Links Pass Pagerank
PageRank is a system used by Google to rank web pages in their search engine results. It is essentially a measure of the importance of website pages based on the quantity and quality of links to them. When your website has a well-structured system of internal links, it can effectively distribute PageRank throughout the site.
Here’s how it works:
- Distribution of PageRank: Each page on your website has a certain amount of PageRank, primarily acquired from external backlinks. When you link one page of your website to another, you pass some of this PageRank to the linked page. This process helps in distributing the accumulated PageRank across various pages of your site, rather than concentrating it in a few areas.
- Boosting Lesser-Seen Pages: Internal linking can be particularly beneficial for pages that don’t naturally attract many external links. By linking to these less visible pages from higher-ranked pages on your site, you can pass some of the PageRank to them. This strategy can boost their visibility and ranking in search results.
- Controlling the Flow of PageRank: Strategic internal linking allows you to direct PageRank to the pages that you deem most important. For example, linking more frequently to your product pages from blog posts or the homepage can increase their PageRank and, as a result, their search engine ranking.
In summary, internal links are not just navigational tools but also crucial in optimizing the flow of PageRank throughout your website. This can significantly impact how your pages rank in search engine results, thereby influencing your website’s overall SEO performance.
What Is Anchor Text and Why It Is Important For SEO?
While executing the internal link strategy, your choice of anchor text plays an important role. But what exactly is an anchor text? Anchor text is the clickable text in a hyperlink. It’s usually highlighted or underlined in a distinctive colour, making it stand out from the rest of the text on a webpage.
Anchor text is significant in SEO (Search Engine Optimization) because it provides context to both users and search engines about the content of the link’s destination.
For example, if you have a blog about gardening and you include a link to a page about plant care, the anchor text might be “How to care for indoor plants.” This specific phrase, when clicked, would lead the user to the linked page. The choice of anchor text is important because:
- Context for Users: It informs the user about what to expect when they click the link. Clear and descriptive anchor text improves the user experience by making navigation intuitive.
- SEO Relevance: Search engines use anchor text to understand the content of the linked page. Relevant and accurate anchor text can help improve a page’s ranking for specific keywords.
What Anchor Text to Use With Internal Linking?
Selecting the right anchor text is more nuanced than it might initially appear. A good rule of thumb is to encapsulate the essence of the linked page in just 3-4 words. Strive to keep the anchor text concise; avoid turning it into a lengthy phrase, a sentence, or a short paragraph.
For instance, if you’re linking to a blog post about content marketing strategy within an article on marketing funnels, an ideal anchor text would be “content marketing strategy.”
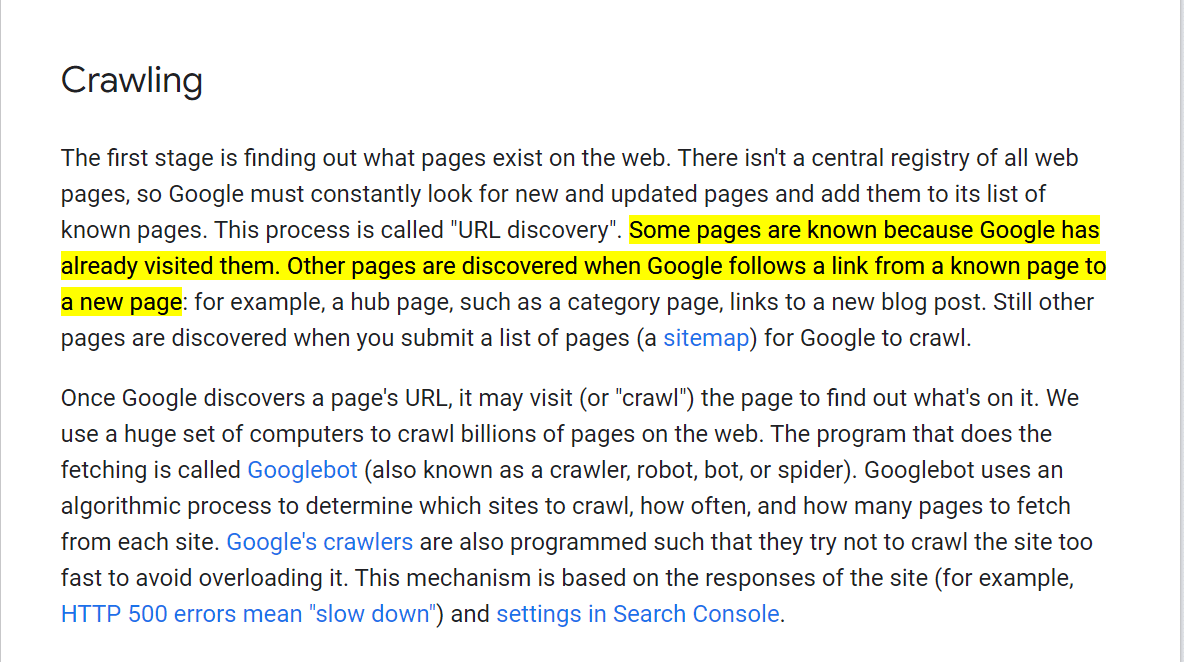
It’s advisable to steer clear of vague anchor texts like “this document,” “this text,” “know more,” “click here,” or “more information.” Similarly, using naked URLs (the direct web address) as anchor text is not recommended. These types of anchor texts are not informative and fail to provide clear insight to both users and search engines about the content of the linked page. Effective anchor text should be descriptive and directly related to the linked content. Google actually state this themselves in their own documentation.
Additionally, when creating internal links with anchor text, it’s important to exclude any punctuation that immediately precedes or follows the link. The punctuation should not be part of the clickable text.
For example, consider the phrase “download the PDF here.” In this case, the anchor text should be “download the PDF here” without including the full stop in the hyperlink.
Notice in the example that the full stop (period) is not part of the anchor text.
12 Internal Linking Best Practices for Better UX and SEO Results
Having gained a clear understanding of what internal links are, their advantages, and the concept of anchor text, you are now well-prepared to develop a strategy. To optimize your website’s SEO with internal linking, follow these best practices.
1. Enhance Site Architecture with Strategic Internal Links
Internal linking is an essential element for enhancing your website’s navigation and structural clarity, complementing the role of a sitemap. While a sitemap lists the pages available for search engines to crawl, internal links add another layer by connecting these pages in a meaningful and organized way. This connection is not just about linking Page A to Page B; it’s about strategically categorizing and structuring content to improve the overall user experience.
In planning your internal linking strategy, focus on integrating all significant pages that contribute to a more cohesive and user-friendly site.
For an eCommerce site, for example, effective internal linking can facilitate user navigation between different product categories, potentially increasing business and revenue. This structured linking makes it easier for users to find what they are looking for, enhancing their overall shopping experience.
For non-eCommerce sites, internal linking plays a crucial role in keeping users engaged, increasing brand awareness, and guiding them through the marketing funnel. By thoughtfully linking related content, you can lead users to discover more about your brand and offerings, fostering deeper engagement and possible conversions.
2. Use Keyword-Rich Anchor Text (but not too often)
Continuing with the best practices for internal linking in SEO, it’s important to focus on using keyword-rich anchor text. Google itself suggests paying special attention to anchor text as it gives both users and search engines an indication of the content on the linked page.
You have the option to use either exact match or partial match anchor text, depending on the context and intention of your link. Exact match anchor text includes the exact keyword or phrase you’re targeting, while partial match incorporates the target keyword along with other words.
However, it’s crucial to avoid overstuffing your anchor text with keywords. This can come across as spammy and might even negatively impact your SEO efforts. Always aim to provide value with your anchor text, ensuring that it aligns with the content of the linked page and genuinely assists users in understanding what to expect when they click the link.
3. Link to Important Pages
As previously mentioned, linking from one page on your site to another effectively transfers some of that page’s authority. This can be likened to an expert in a particular field endorsing a certain topic, which in turn elevates the credibility of the endorsed topic. Search engines view this transfer of authority in a similar light.
To effectively link your most important pages, you can follow these steps:
- Identify the High-Performing Pages: Start by pinpointing the pages on your website that perform the best in terms of traffic, engagement, or conversions.
- Create Strategic Links: Once you’ve identified these high-performing pages, strategically create links from these pages to the ones you want to boost in terms of ranking.
By doing this, you’re leveraging the existing authority of your top pages to elevate the importance of other key pages in the eyes of search engines. This method of internal linking not only helps in distributing page authority more evenly across your site but also enhances the visibility of lesser-known pages.
4. Consider the Page Location of Your Internal Link
The placement of an internal link on a page is more significant than you might think. Google uses the “Reasonable Surfer Model,” which is a part of its patented method for ranking pages. This model assesses the likelihood of a link being clicked by a user, based on its position on the page and other factors.
According to this model, a link’s position can greatly influence its chances of being clicked and, consequently, its ability to pass value or “equity.” Links placed higher up on a page are typically more likely to be clicked, and as per the model, they tend to pass more equity.
Thus, when placing internal links on your website, it’s beneficial to position them higher on the page, but only in contexts where they naturally fit. This strategic placement not only caters to user browsing habits but also aligns with how Google’s algorithm values and assesses links. The focus should always be on maintaining relevance and enhancing the user experience.
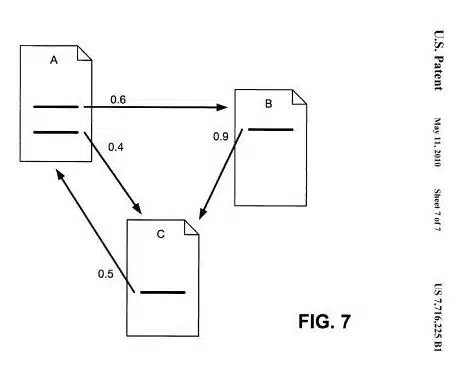
We talk more about the reasonable surfer model in this guide.
5. Consider Intent and Relevancy
When adding internal links to your website, the emphasis should be on the relevance and context of each link, rather than its physical location on the page. The true value of an internal link lies in how appropriately it fits within the content and whether it genuinely serves the user’s interests.
It’s crucial to focus on enhancing the user experience by embedding links that are inherently related to and complement the surrounding content. Randomly inserting links without considering their relevance can disrupt the user experience, potentially diminishing trust and engagement.
A practical approach is to meticulously go through your content, pinpointing places where you can naturally introduce additional, pertinent information that aligns with what your audience is seeking. For instance, consider a blog post about healthy eating habits. In a section discussing the benefits of a balanced diet, a well-placed internal link to a page with detailed meal plans or a collection of healthy recipes would be highly relevant and beneficial to the reader.
This method ensures that each internal link you incorporate not only fits seamlessly with the content but also enriches the reader’s experience, encouraging deeper interaction with your website.
6. Point Internal Links From Traffic Pages to Conversion Pages
Many websites experience a common issue: they attract a significant amount of traffic to their blog pages, but struggle with conversions. A strategic way to address this challenge is by interlinking pages that receive high traffic with those designed for conversions. This approach can significantly impact your business outcomes.
Here’s a step-by-step method to effectively link high-traffic pages to your conversion pages:
- Utilize Google Analytics: Start by opening Google Analytics. Navigate to Reports, then to Engagement, and finally to Pages and screens.
- Identify Top-Performing Pages: Within this section, you’ll find a list of your site’s top 10 pages, ranked by page views.
- Customize Metrics: Use the dropdown options to tailor the metrics. Filter the report to focus specifically on certain categories of pages, such as blog posts, if that’s your area of high traffic.
- Locate Target Conversion Pages: Similarly, identify the pages on your site that you aim to drive more traffic to for conversions. These are the pages where you want visitors to take action, such as making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or filling out a contact form.
- Create Strategic Internal Links: Once you’ve identified these high-traffic and target conversion pages, start interlinking them. Place links on your high-traffic pages that lead directly to your conversion pages.
By implementing this strategy, you create a pathway for visitors from your most visited content to the pages where they can engage further with your business. This not only increases the likelihood of conversions but also maximizes the value of your existing traffic.
7. Build internal links for orphan pages
Search engine crawlers find it incredibly difficult to find orphan pages. Orphan pages are pages that don’t have any internal links pointing to them. By creating internal links to these orphan pages from well-established and authoritative pages on your site, you can significantly enhance their visibility and improve their potential rankings in search engine results.
Here’s how you can address orphan pages:
- Identify Orphan Pages: Use a tool like Screaming Frog to scan your website and identify any orphan pages. These are pages that aren’t linked to from other parts of your site, which makes them harder for search engine crawlers to find and index.
- Analyze Your Sitemap: Review your sitemap to understand the structure of your website and find content that is relevant to your orphan pages. Your sitemap will provide a clear overview of how your current pages are interlinked.
- Create Strategic Internal Links: Once you have identified the orphan pages and relevant content, start creating internal links. Link from your high-authority pages to the orphan pages, and consider adding links on the orphan pages that lead to other relevant sections of your site.
- Incorporate Links in Both Directions: It’s not just about linking to the orphan pages; also consider how these pages can link back to other parts of your website. This creates a two-way connection that further integrates these previously isolated pages into the overall structure of your site.
By following these steps, you can ensure that all your pages, including the orphan ones, are woven into the fabric of your site’s internal link structure. This not only aids in better indexing by search engines but also improves the overall user experience by making all your content more accessible.
We’ve written a more detailed guide on orphan pages and how to fix them here.
8. Link Old Posts to New Posts And Vice Versa
Linking older posts to newer ones and vice versa is a highly effective internal linking strategy. It not only enhances user engagement by providing more comprehensive content but also helps in improving the SEO of both new and old posts. Here’s how you can implement this approach:
Internal Linking in Old Posts:
- Select High-Performing Old Posts: Begin by identifying older blog posts that are already performing well in terms of traffic and Google rankings.
- Compile a List of Linkable Content: Prepare a list of newer blog posts that are relevant and could be linked from these older posts.
- Strategically Place Links: Go through the selected old posts and determine the most appropriate spots to insert internal links. Ensure that the anchor text used is relevant and accurately reflects the content of the linked post.
Internal Linking in New Posts:
When it comes to new posts, the primary objective of internal linking should be to guide users to related content, enhancing their understanding of a topic. While this may also increase traffic to older posts, the focus should be on user enrichment.
- Review New Content: As you create or review new posts, carefully scan through the content.
- Identify Opportunities for Links: Look for opportunities to insert links to older, relevant posts. These links should feel natural and contextually fit within the content.
- Use Appropriate Anchor Texts: Choose anchor texts that are descriptive and give users a clear idea of what to expect when they click the link.
By effectively linking old posts to new ones and vice versa, you create a more interconnected and user-friendly content experience on your website. This not only helps keep the audience engaged but also allows for better circulation of traffic across different pages of your site
9. Use Different Anchor Texts for The Same Page Across Different Pages
Using varied anchor text is beneficial for SEO, as it assists Google in understanding the content of the linked page. Diversifying your anchor text can be particularly effective for encompassing a range of long-tail keywords, as long as they share similar intent and relevance to the linked content. This approach enables you to target different keyword variations while maintaining relevance and context.
When selecting anchor text, consider using a broad match variation that aligns with both the context of your content and the search intent of your audience. This means choosing anchor texts that are not just exact matches of your target keywords but also include variations or related phrases. Such a strategy ensures that your internal linking is not only SEO-friendly but also user-friendly, providing clear and varied pathways for users to explore related content on your site.
10. Deep Linking
While planning and executing your internal link strategy, ensure you explore link opportunities deep within your site structure and not repeat the pages already included in your site’s main navigation.
Think of case studies, blog pages, services pages, about us pages, and testimonial pages to boost the overall SEO performance of your site.
11. Add the “Related Posts” Section in Blogs
If you have seen some of the major publications and authority websites like Search Engine Journal and Hubspot, you will find that their blog posts have small sections for “Related Posts” on their blog pages.
As you can see above, the Search Engine Journal has listed suggested articles at the end of their blogs to help users navigate through relevant content.
In this example, HubSpot has internally linked a few blogs in between the content so users can carry on their exploration if they wish.
Having a “Related posts” or “Suggested Articles” section is an amazing way to show your posts to more visitors. You can use online plugins and tools for that, but if you want to have better-quality suggestions, we recommend doing it manually.
12. Fix Broken Links
Fixing broken links is essential for SEO, particularly in larger or older websites where issues like redirect chains can be more prevalent. To improve PageRank, user experience, and crawl efficiency:
- Identify Broken Links: Use tools like Google Analytics or Screaming Frog to find broken links on your site.
- Repair or Replace: Update the URLs of broken links or replace them with relevant, active pages.
- Update Anchor Texts: When changing a link’s URL, also update its anchor text to avoid sending mixed signals to Google about the content of the destination page.
Regularly addressing broken links is crucial for maintaining a seamless user experience and optimizing your site’s SEO performance.
What Not To Do While Interlinking?
1. Don’t Limit Your Interlinks To Navigation, Footers and Sidebar
Avoid restricting your internal links to just the navigation, footer, and sidebar areas. While these are key places for links, they shouldn’t be the sole focus. Overemphasizing these areas can limit user engagement and SEO opportunities. Instead, integrate internal links within your main content where they can provide context and add value, guiding users to related topics or services naturally. This approach enhances the user experience and improves your site’s overall connectivity.
2. Don’t Link to Different Pages With The Same Anchor Text
Using two different pages with the same anchor text confuses Google and may harm your rankings.
For example, if you have two pages – “content marketing services” and “content audit services”, you shouldn’t link to both pages with the same anchor text of “content services.”
Be as specific as possible about the anchor text so Google and users know what exactly you are talking about and how those two (or multiple) pages differ.
3. Avoid Over-Optimization
Resist the temptation to cram your pages with an excessive number of internal links. While it might seem like a good strategy to reduce bounce rates, enhance conversions, and maximize value, overdoing it can backfire. Over-optimization of internal links can lead to a diluted PageRank and give your content a spammy appearance. Furthermore, presenting users with too many choices can be counterproductive, as it may overwhelm them, leading to a reluctance to click on any of the links.
There’s no definitive “ideal” number of internal links per page; the key is to ensure that each link is meaningful and contributes value, rather than just existing for the sake of linking. Aim for a balance where your internal links enhance the user experience and the content’s value without overwhelming the page.
4. Avoid Linking to a Dead-end and Redirect Loops
One thing you want to make sure of while you interlink is not leading your users and Google to a dead-end. For example, redirecting them to 404 errors or non-existing pages when they click on an internal link.
Additionally, when linking between two pages, ensure you are not creating a loop where one page redirects back to itself. Redirect loops harm your SEO efforts as search engines don’t know how often they should follow the redirects before reaching the final destination.
Lastly, avoid building internal links to your home page as it will already have many points linking toward it; instead, focus on other important pages that need it more.
5. Avoid Links in Submission-required Forms And Internal Search Boxes
It’s advisable not to embed important links or content within submission-required forms or internal search boxes on your site. These elements, which may range from simple dropdown menus to comprehensive surveys, require human interaction for their operation. Since Google’s crawlers don’t attempt to submit forms or use search boxes, they won’t be able to discover or index any content or links placed within these areas. Consequently, placing internal links in such locations is ineffective for SEO purposes, as these links will remain unseen and unindexed by search engines. For optimal site indexing and user experience, keep important links within the main content areas of your website.
Regularly Update And Maintain Internal Links for The Best Results
Don’t treat internal linking as a one-off task. Continually applying SEO best practices, including regularly reviewing and updating your internal links, is crucial for optimal results. Neglecting this ongoing maintenance can significantly diminish the effectiveness of your internal linking strategy. Remember, consistent upkeep is key to completing the full SEO circle.
For help producing content quickly, remember to check out our AI Writing Assistant.
FAQs
What is an Internal Link? And How Is It Different From an External Link?
An internal link is a hyperlink that connects one page to another within the same website or domain. In contrast, external links connect two pages on the internet from different domains.
How Does Internal Linking Help SEO?
Internal linking aids SEO by improving website structure and user experience. It helps search engines understand your site’s content hierarchy and relevance, potentially leading to better rankings.
How Do You Find Internal Linking Opportunities?
To find internal linking opportunities, start by reviewing your existing content. Identify keywords and phrases within your articles or pages relevant to other content on your website. Then, link these keywords or phrases to your site’s related pages or articles. Use content audit tools or plugins to analyze your website for potential linking opportunities. Lastly, consider creating pillar content or hub pages that can be central points for linking to other related pages, enhancing the overall user experience.
Do Internal Links Help SEO?
Yes, internal links are beneficial for SEO. They distribute link authority, make your content more accessible to users and search engines, and signal content relevance, which can improve search rankings.
How Many Internal Links Should You Have on Your Page?
The number of internal links should feel natural and relevant to the content. There’s no specific quota but focus on adding links that genuinely enhance the user’s journey and understanding.
What is an Example of Internal Linking?
An example of internal linking is linking from a blog post discussing “SEO tips” to another page that delves deeper into “On-Page SEO Best Practices” on the same website.
Are Internal Links Backlinks?
No, internal links connect pages within the same website. Backlinks, on the other hand, come from external websites and point to your site’s pages.
What is the Best Internal Linking Strategy for SEO?
The best strategy prioritizes user experience and relevance. Use descriptive anchor text, maintain a logical site structure, and ensure links genuinely benefit users.
Can I add an internal link to the page itself?
Technically, you can, but it’s generally not recommended unless it serves a specific user or content organization purpose. Internal links should often direct users to different pages within the same site.
Start your trial today for only $1
Sign up today for a $1 trial and enjoy access to 6000 keyword clustering credits, 3 Keyword discovery searches, 1 Content Brief and Pro versions of SERP Similarity, SERP Explorer.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Subscribe to get our latest news, offers, insights, and any updates.

